Data Normalization
In the simplest cases, normalization of ratings means adjusting values measured on different scales to a notionally common scale, often prior to averaging.
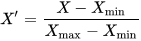
Feature scaling is used to bring all values into the range [0,1]. This is also called unity-based normalization.
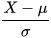
Normalizing errors when population parameters are known. Works well for populations that are normally distributed
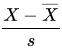
the departure of the estimated value of a parameter from its hypothesized value, normalized by its standard error.
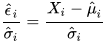
Normalizing residuals when parameters are estimated, particularly across different data points in regression analysis.
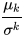
Normalizing moments, using the standard deviation sigma as a measure of scale.
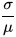
Normalizing dispersion, using the mean mu as a measure of scale, particularly for positive distribution such as the exponential distribution and Poisson distribution.